
You’ll probably need an X-ray image, too. To diagnose a fibular fracture, your healthcare provider will examine the site of the injury, the knee joint, and the ankle joint. See a doctor if you have symptoms of a fracture, especially after a traumatic injury.
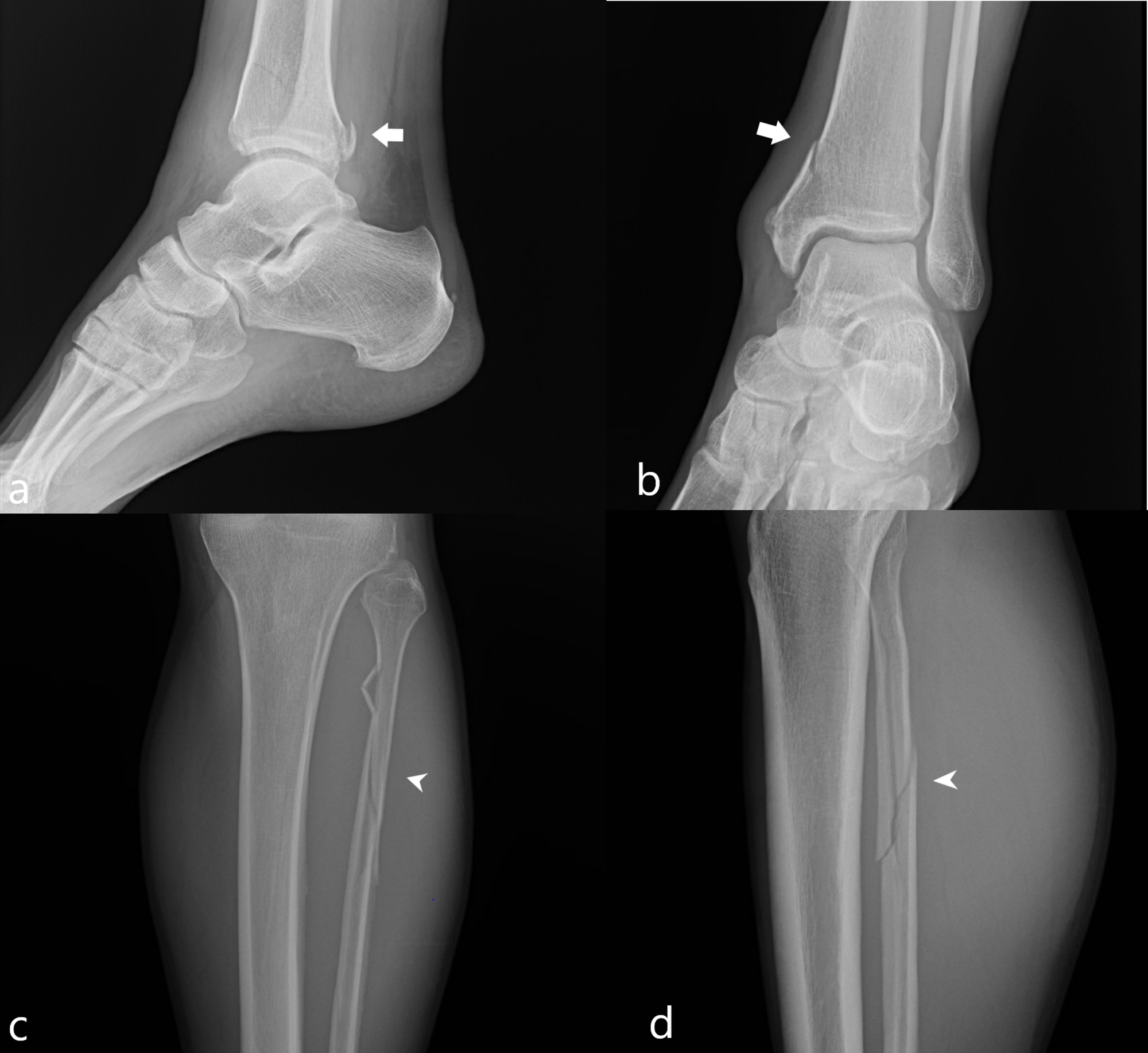
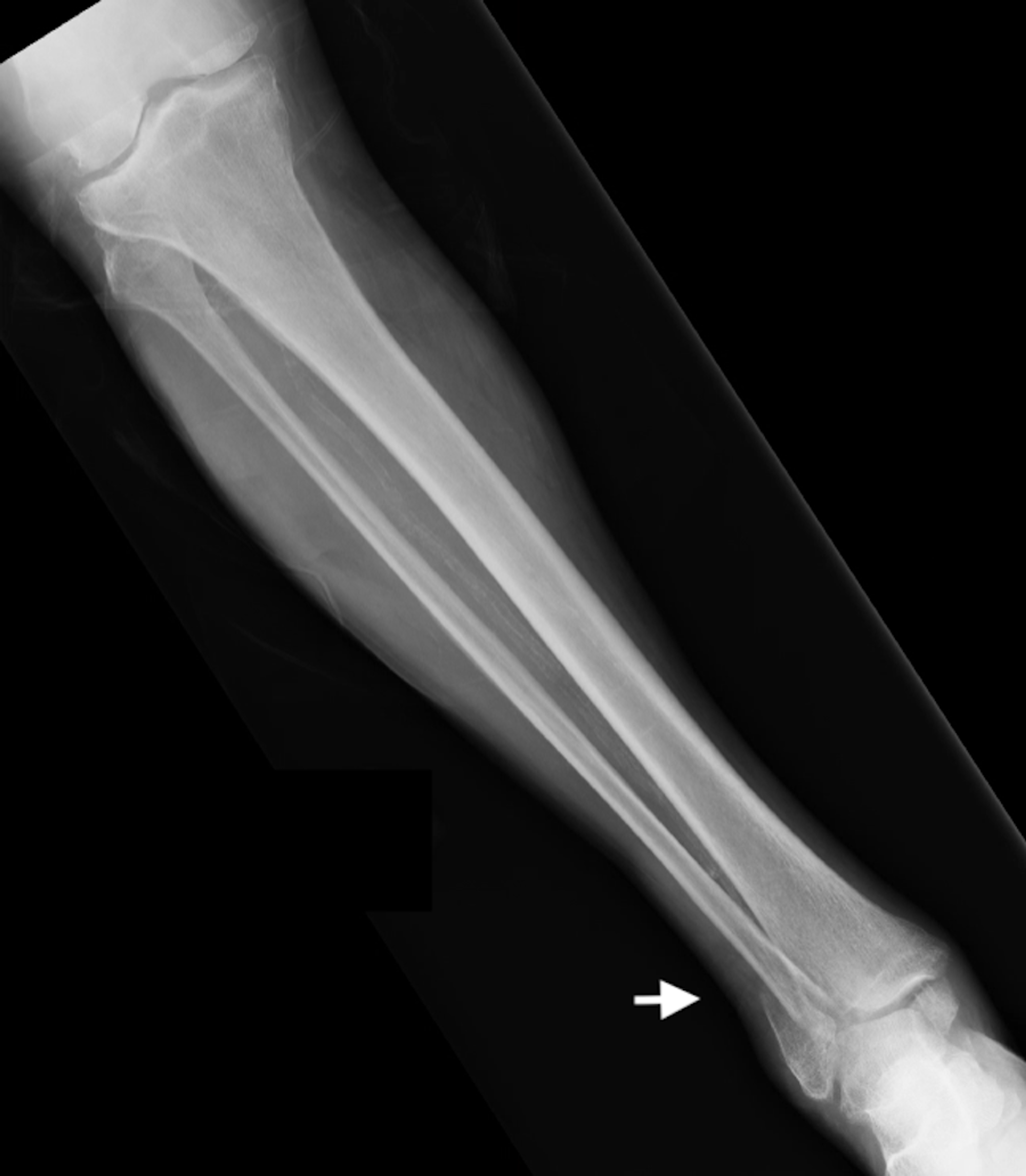
Fibular fractures are usually caused by: This can happen when you roll your ankle, have a direct blow to the leg, fall, or experience sports-related trauma. Shaft Fracture, a break that often affects the middle of the leg due to direct impactĮxcept for stress fractures, these fractures often occur due to a traumatic injury or more pressure placed on the bone than it can handle.Stress Fracture, a hairline fracture due to repetitive injury.Avulsion Fracture, a fracture in which a small part of the bone gets pulled off.Fibular Head Fracture, a break near the knee.Lateral Malleolus Fracture, a break around the ankle.
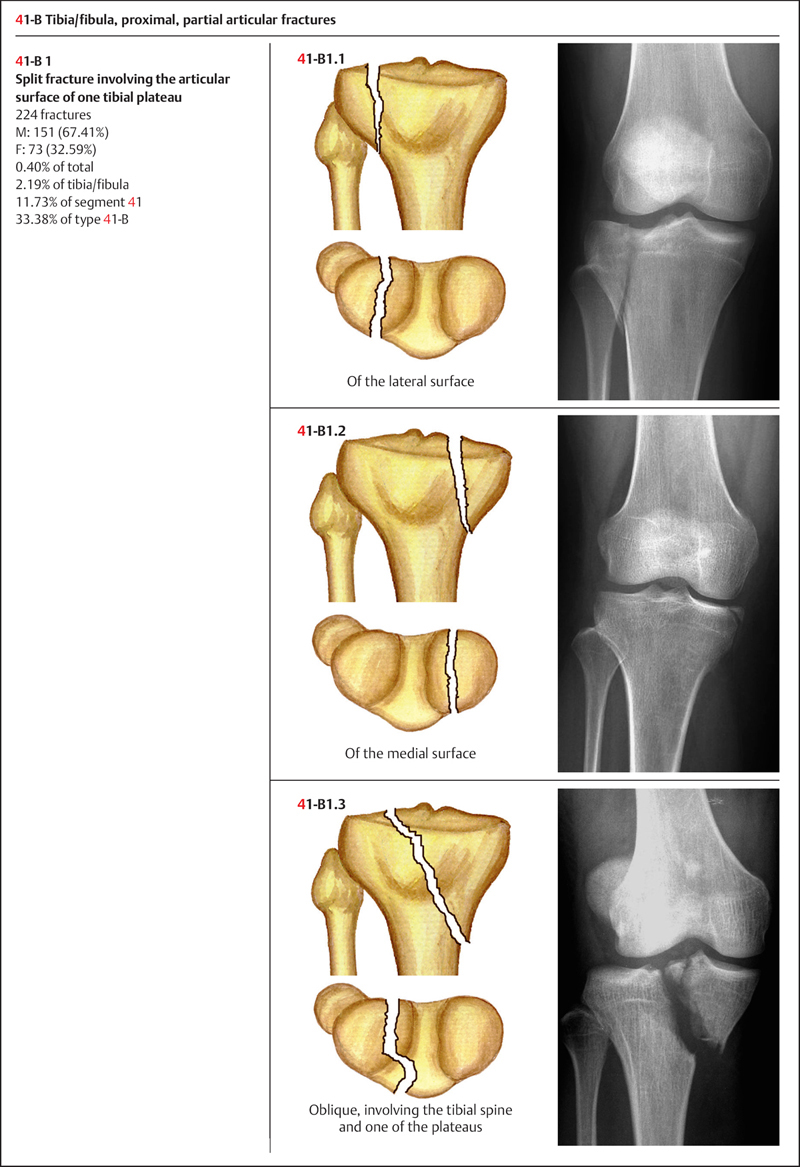
There are different types of fractures, which can also affect treatment and recovery. In the elderly population, slipped and fall is the cause of fibula bone fracture. Downhill skier, snowboarding, and skiers have high rates of fibula bone fractures as well. The injury is common in athlete who is engaged in collision or contact sport such as soccer, football, basketball, rugby and Lacrosse. Fibula fractures occur around the ankle, knee, and middle of the leg. Types of Fibula Fracturesįractures and breaks refer to the same condition. The mechanism of transferring ground reaction forces occurs due to muscles attachments on the upper part of the fibula bone underneath the knee. Moreover, it transfers forces as the ankle hits the ground during walking. The fibula bone bears only 15 to 20% of the body weight. The tibia bears approximately 80% of the body weight. The fibula bone plays a minor role in bearing the weight of the body as we walk. The fibula can bend slightly and it can also rotate within its ligament. The ligaments and the interosseous membrane have a little flexibility in them, to allow the ankle joint and the two bones to move during walking and motion of the ankle. There is also a soft tissue in between the two bones, called the interosseous membrane, which runs the length of the two bones and binds the two bones together to keep them stable. The tibia and fibula are connected by ligaments underneath the knee and at the ankle. It forms the base of the knee called the tibial plateau and extends down to form the inside of the ankle joint. Next to the fibula bone is the tibia, which is thicker. The fibula is a slender and long bone located on the outside of the lower leg, from outside and underneath the knee and extends down to form the outside of the ankle joint.
#Proximal and distal fibula fracture skin
Seek emergency medical attention if you think you might have a fracture, particularly if the fracture breaks skin and bone is visible. A fibula fracture happens when more pressure is put on the bone than it can handle. The fibula only carries 17 percent of the body’s weight. However, this bone has no significant role in supporting the body weight. Instead, the fibula helps stabilize and support your leg, body, ankle, and leg muscles. The fibula is a long and thin bone runs parallel to the tibia, a larger bone that also forms the shin, and attaches the ankle and knee joint. The bone outside the leg is the fibula, which is the smaller one. Most of the weight of the body is carried by the tibia (the larger bone of the lower leg).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
