
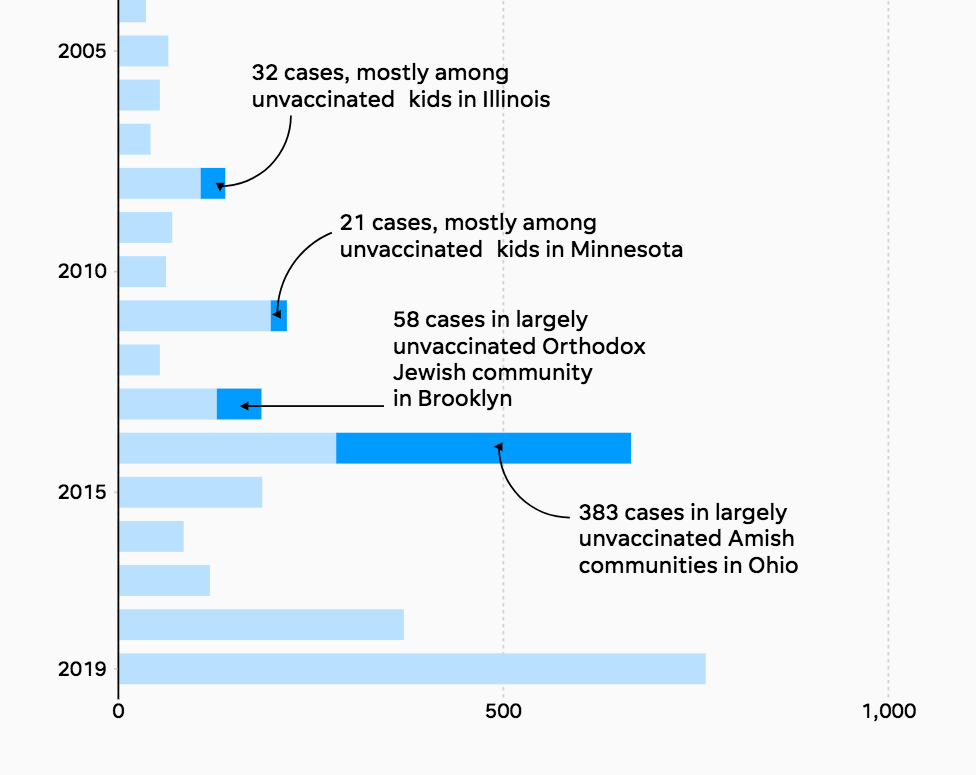
The highest risk is during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. Up to 2 in 100 infants exposed to chickenpox before birth are born with congenital varicella syndrome and may have skin scarring, eye, limb and brain abnormalities, developmental delay and a poor outcome. Pregnant womenĬhickenpox during pregnancy can spread to your baby. Untreated bacterial skin infections can lead to bacterial infection in other parts of your body, including pneumonia and blood stream infection (septicaemia). Other complications of chickenpox are rare and include encephalitis (brain inflammation) and inflammation of your joints, kidneys and liver.Ĭhickenpox tends to be more severe in adolescents and adults, pregnant women and their unborn babies and people of any age with poorly functioning immune systems. Around 1 in 20 healthy children develop a bacterial skin infection from chickenpox, which needs antibiotic medicine. In most people, chickenpox is a mild disease that doesn't cause any lasting problems. Live attenuated vaccines given by injection are generally effective after one dose.Ĭhickenpox – Disease and Vaccine, New Zealand When a live attenuated vaccine does cause any illness, it is usually milder than if you had caught the disease. Live attenuated vaccines don't usually cause disease in vaccinated people who have a healthy immune system. This means a very small dose of virus is given to stimulate a response by your immune system. The chickenpox vaccine is a live vaccine which is made using chickenpox viruses that have been weakened (or attenuated), before being included in the vaccine. After vaccination, the weakened vaccine viruses replicate (grow) inside you. This is to protect against shingles and is not given to children. Note: There is another varicella vaccine called Zostavax®. You can even catch the chickenpox virus from touching clothing or other objects that have fluid from the blister on them. It is important to adequately rest as needed after a COVID-19 vaccine.Chickenpox vaccine protects against infection from the varicella zoster virus, which causes chickenpox infection. The virus is easily spread by sneezing and coughing, or by contact with weeping chickenpox blisters. Sometimes these flu-like side effects can mean that people struggle to carry out their usual activities for a day or so. The most common side effects for both vaccines include: Currently two COVID-19 vaccines are being used in Australia: the Pfizer vaccine and the AsraZeneca vaccine. Usually these are mild and go away without treatment in 1–2 days. Like other vaccines, COVID-19 vaccines can also cause side effects. your symptoms are not improving or getting worse.your baby has sudden unusual screaming episodes with vomiting or blood in the bowel motion.paracetamol or ibuprofen is not relieving the fever, particularly for babies and infants.You or your child need to see a doctor if: They should keep drinking plenty of oral fluids, preferably water.

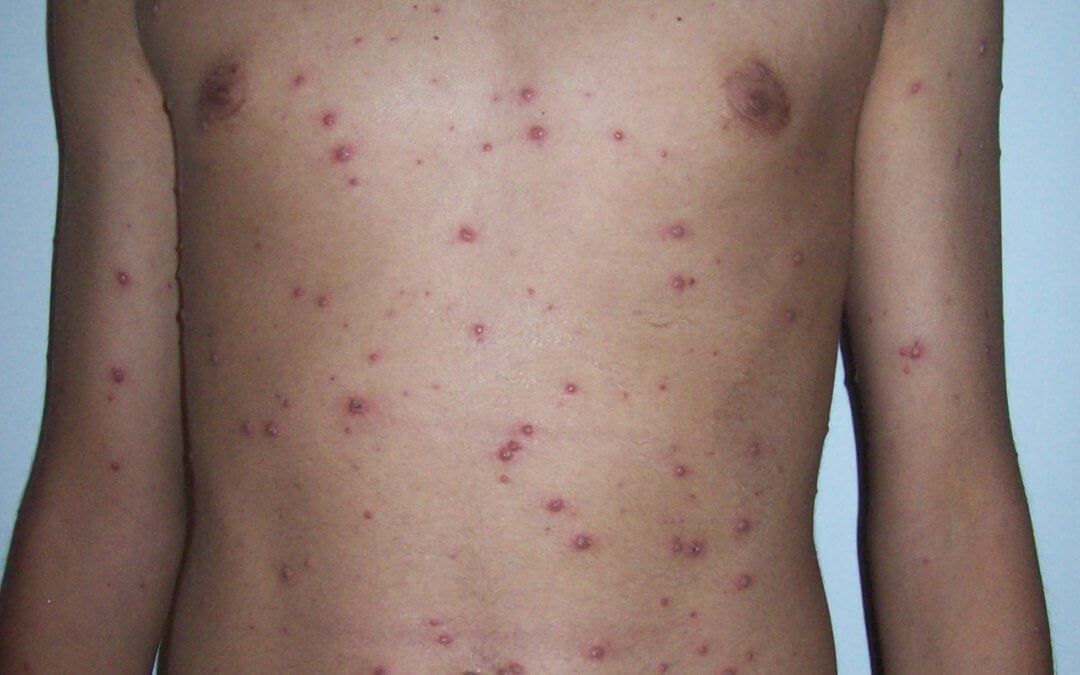
This rash is not contagious.Īfter an older child or an adult gets a vaccine, they may experience some mild and temporary side effects: a rash after MMR or chicken pox vaccine.feel hot and have a temperature >38 degrees.This usually does not require any treatment. slightly red, itchy or sore legs or arm for a day or two.You can get more information about Rotarix vaccination here. mild diarrhoea or a few vomits after the oral Rotarix vaccine which sometimes may last up to a week.slightly unsettled and cry a little more than usual.Babies and infantsĪfter a baby or an infant gets a vaccine, they may experience some mild and temporary side effects:

Usually these are mild and go away on their own after 2–3 days. Some people may experience side effects, or adverse events, after getting a vaccine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
